Render markdown cells using MyST Markdown, including support for rich frontmatter, interactive references, admonitions, figure numbering, tabs, cards, and grids!
Requirements¶
JupyterLab >= 4.0
Install¶
To install the extension, execute:
pip install jupyterlab_mystFeatures¶
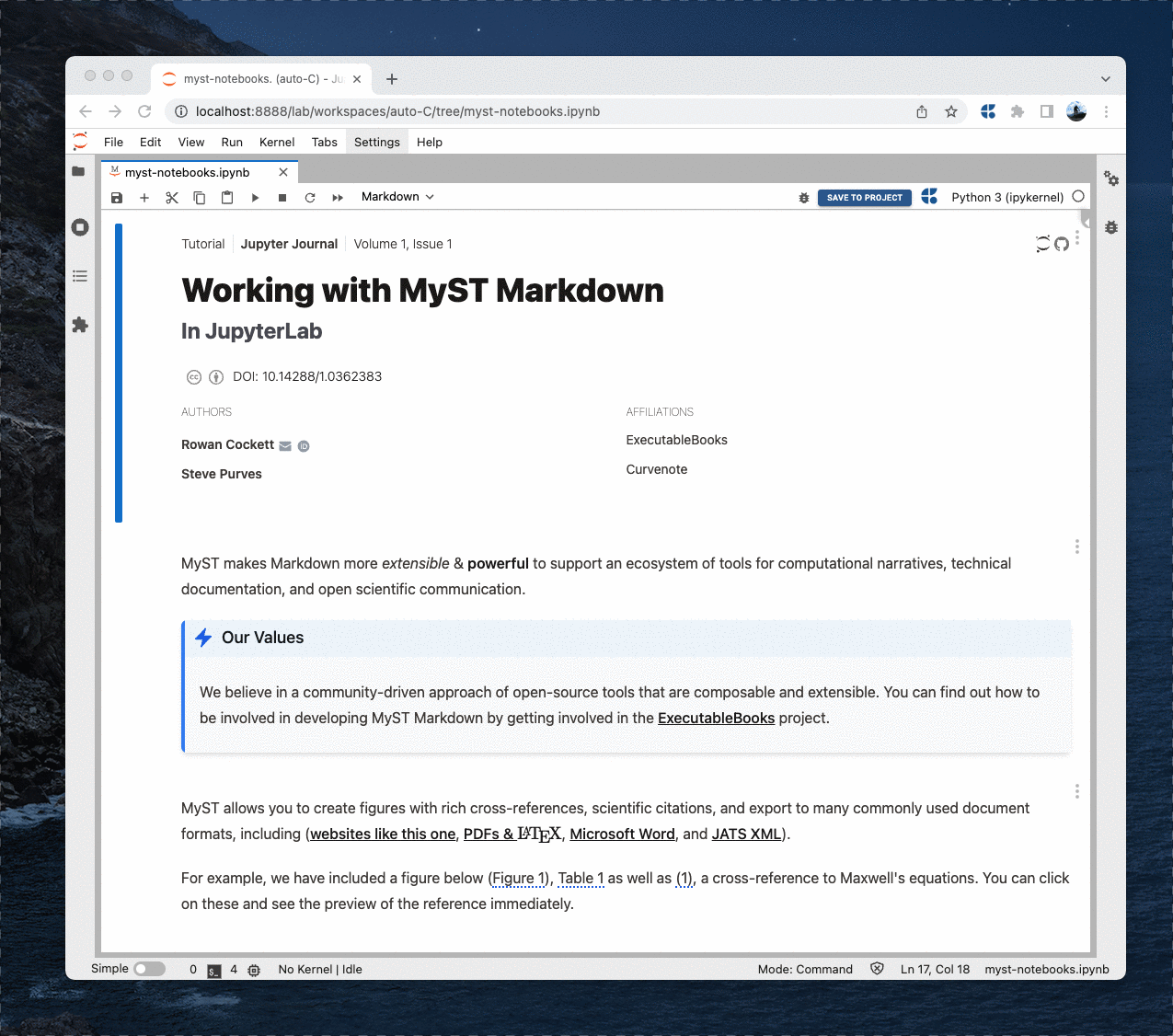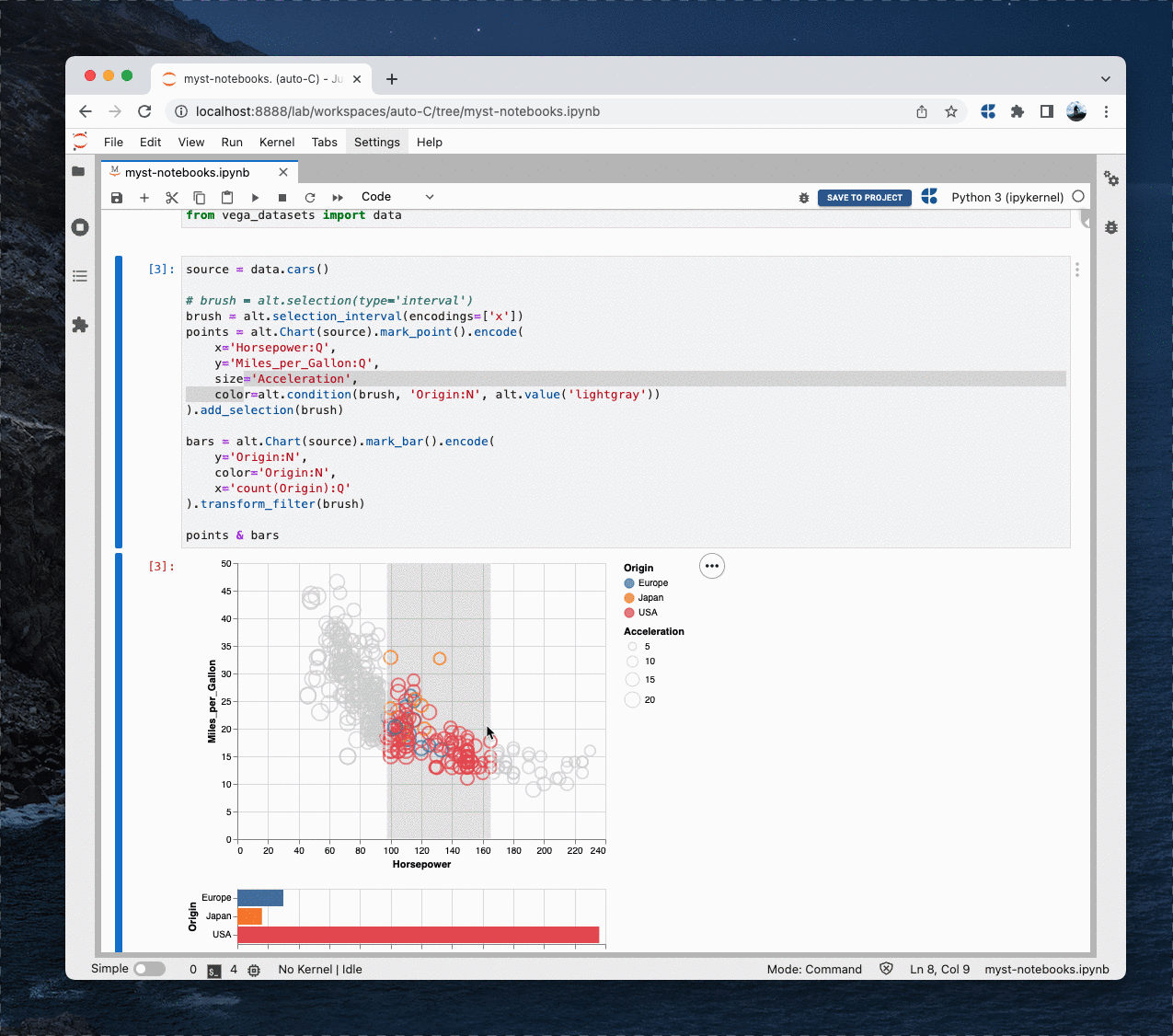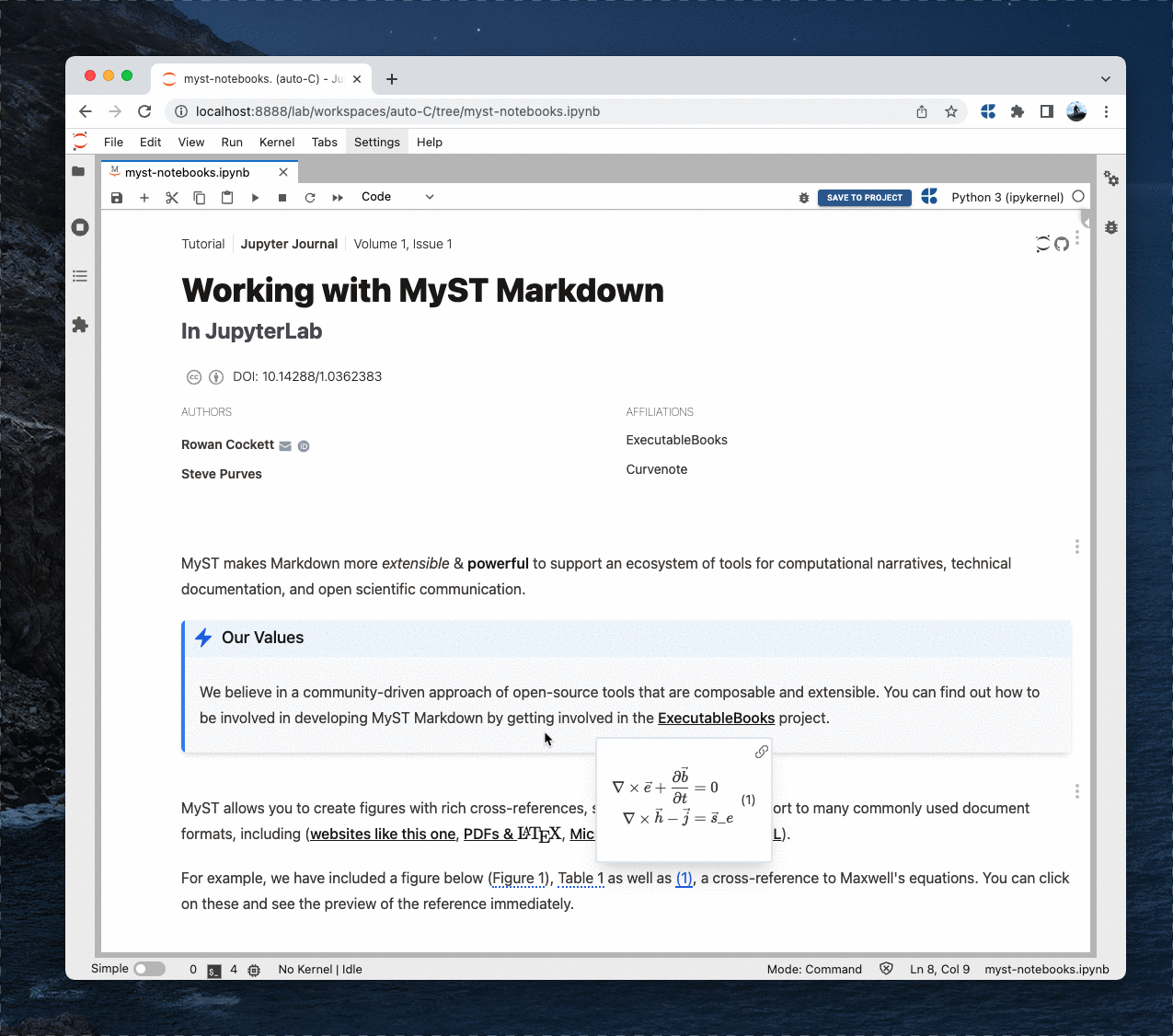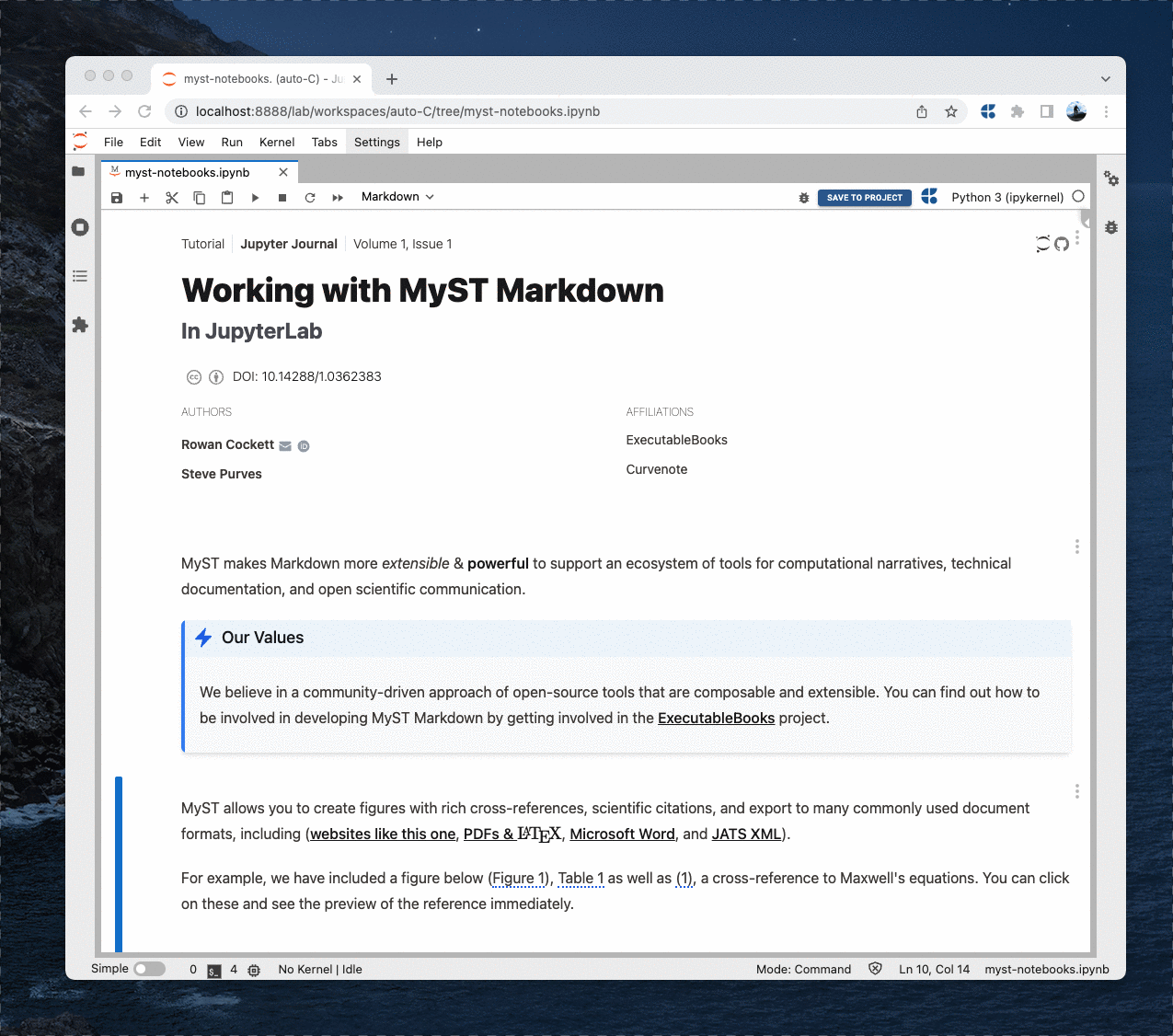
jupyterlab-myst is a fully featured markdown renderer for technical documents, get started with MyST Markdown. It supports the MyST {eval} inline role, which facilitates the interweaving of code outputs and prose. For example, we can use inline expressions to explore the properties of a NumPy array.
In the code cell:
import numpy as np
array = np.arange(4)In the markdown cell:
Let's consider the following array: {eval}`array`.
We can compute the total: {eval}`array.sum()` and the maximum value is {eval}`array.max()`.This will evaluate inline, and show:
Let's consider the following array: array([0, 1, 2, 3]).
We can compute the total: 6 and the maximum value is 3.You can also use this with ipywidgets, and have inline interactive text:
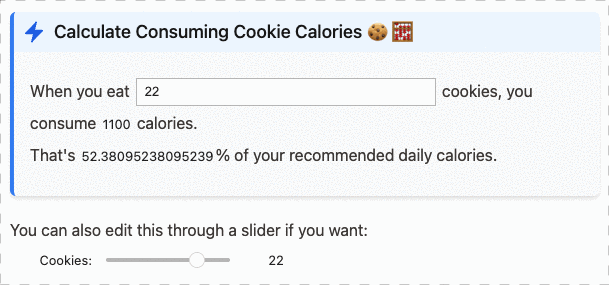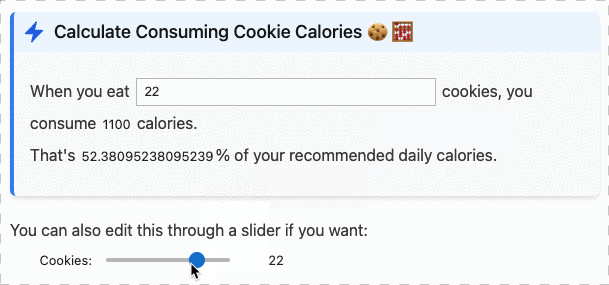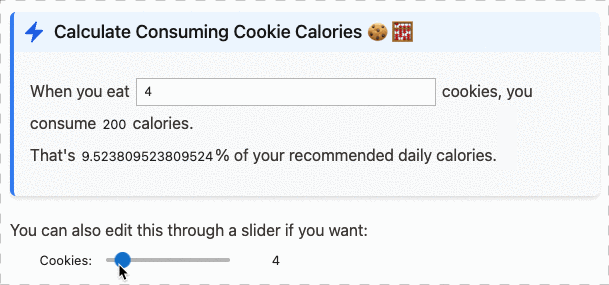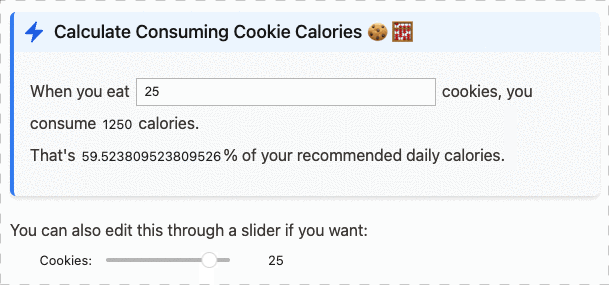
Or with matplotlib to show inline spark-lines:

You can also edit task-lists directly in the rendered markdown.

Usage¶
MyST is a flavour of Markdown, which combines the experience of writing Markdown with the programmable extensibility of reStructuredText. This extension for JupyterLab makes it easier to develop rich, computational narratives, technical documentation, and open scientific communication.
Execution 🚀¶
To facilitate inline expressions, jupyterlab-myst defines a jupyterlab-myst:executor plugin. This plugin sends expression code fragments to the active kernel when the user “executes” a Markdown cell. To disable this functionality, disable the jupyterlab-myst:executor plugin with:
jupyter labextension disable jupyterlab-myst:executorTrust 🕵️♀️¶
Jupyter Notebooks implement a trust-based security model. With the addition of inline expressions, Markdown cells are now considered when determining whether a given notebook is “trusted”. Any Markdown cell with inline-expression metadata (with display data) is considered “untrusted”. Like outputs, expression results are rendered using safe renderers if the cell is not considered trusted. Executing the notebook will cause each cell to be considered trusted.
To facilitate this extension of the trust model, the jupyterlab_myst server extension replaces the NotebookNotary from nbformat with MySTNotebookNotary. This can be disabled with
jupyter server extension disable jupyterlab-mystThe MySTNotebookNotary adds additional code that makes it possible to mark Markdown cells as trusted.
Uninstall¶
To remove the extension, execute:
pip uninstall jupyterlab_myst