The instructions on this page guide you through the process of:
making your own book by creating a (new) GitHub repository from a template repository,
making an edit to your book,
“building” your book and viewing it in a web browser via a local server and/or online with GitHub pages.
Create a repository¶
Follow these instruction to use the GitHub template repository to create your own book for this workshop:
Go to the repository for this book
Click the green button
use this templateand clickcreate a new repository.Choose a proper name of your repository (this will be also part of your URL!) and choose the option
public.In your repository, click on
settingsand in the left menu on Pages and chooseGithub Actions
Figure 1:Follow these steps to create your own repository from the template.
Click on
codeand click on thegear-icon(near About) at the right site of the page.Check the box Use your GitHub Pages website.
Go to
Actionsin the top menu, click on the (red)initial commitand clickre-run all jobs
The book will now be deployed again - where now it can actually load GitHub pages.
Figure 2:Follow these steps to create your own GH Pages site from the template.
View your book online¶
The previous stps set up your repository with GitHub Pages, which a GitHub Actions workflow to automatically build your book (a website) and deploy it online. The URL of your book is based on your GitHub username:
https://USERNAME.github.io/workshop-templateThis is, in fact, how the website for this document is created:
https://
You can also find the link easily from you GitHub repository home page under the “About” section on the right-hand side (illustrated in Figure 4).
The home page of your new book website should look like Figure 3.

Figure 3:The home page of your new site, which you can visit once the GitHub Action workflow has successfully completed.
Repo folder structure¶
Your GitHub repository may look similar to the one shown in Figure 4; note the following directories:
content: the source files of your book (in markdown or jupyter notebook format),content/figures: the folder which includes figures for your book,content/lessons: the folder which includes the lessons of this workshop,.github/workflows: the folder which includes the GitHub Actions (automated workflows) to build and deploy your book,css: a folder which includes a custom css file to change the layout of your book,A
myst.ymlfile which defines the structure and settings of your Jupyter Book.
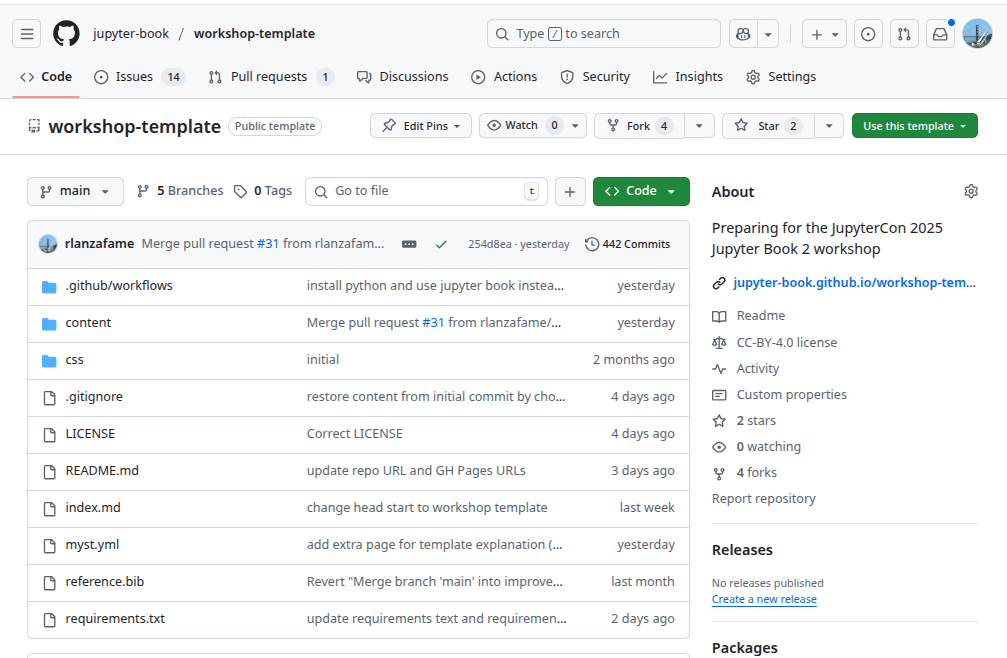
Figure 4:Illustration of repository folder structure.
As proceed through the workshop you will edit the files in your new repository.
Edit the book¶
You have a number of options for making changes to the book’s source and seeing how they affect the output.
Clone the repository to your local machine using Git.
git clone git@github.com:<github_user_name>/workshop-template.gitInstall Jupyter Book, using the virtual environment manager of your choice (all of the tools used today can easily be handled using
pip)
pip install -r requirements.txtMake a change to one of the files in the
contentdirectory using a text editor.(optional) Commit the the change using Git and push it to the remote repository (this will trigger the GitHub Actions workflow and rebuild the website, which can be viewed at the same URL described above). If you go back to your repository and click on the
Actionstab you will see that the workflow is running to build and deploy your book. After a few minutes, you can refresh your book page and see your changes!Build the book from source and serve it locally.
jupyter book startPreview the book in your browser at
http://localhost:3000
To work online, you must “edit” a file by making a commit using GitHub’s online tools:
Click on the
index.mdfile in the Content folderClick on the drop down icon next to the pencil icon and choose
open in github.devThis will start the GitHub development environment where you can edit the files directly in your browser.Edit the file by replacing the names with your own and commit your changes, see Figure 5
Figure 5:Working directly in the GitHub development environment.
Now, if you go back to your repository and click on the Actions tab you will see that the workflow is running to build and deploy your book. After a few minutes, you can refresh your book page and see your changes!
Create a PDF export¶
A clear advantage of JB2 over JB1 is the ability to easily create a high quality PDF export of your book (as well as other formats). In a later lesson of this workshop, we will build a PDF locally and/or modify the GitHb Action workflow to automatically create a PDF export of your book using Typst when changes are pushed changes to your repository.